

Pandas all() method is used to check whether all the elements of a DataFrame are zero or not. It returns either series or DataFrame containing True and False values, if the level parameter is specified then it returns DataFrame, Series otherwise.
We can check DataFrame elements to its axis, either based on row or column by specifying the axis parameter in the pandas.DataFrame.all() method.
Let's understand it by using examples. The syntax of this method is here.
DataFrame.all(axis=0, bool_only=None, skipna=True, level=None, **kwargs)
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| axis | int | 0 | No | {0 or ‘index’, 1 or ‘columns’, None} |
| bool_only | bool | None | No | It includes only boolean columns. If None, will attempt to use everything, then use only boolean data. Not implemented for Series. |
| skipna | bool | True | No | It is used to exclude NA/null values in the DataFrame. If the entire row/column is NA and skipna is True, then the result will be True, as for an empty row/column. If skipna is False, then NA is treated as True, because these are not equal to zero. |
| level | int or level name | None | No | If the axis is a MultiIndex (hierarchical), count along with a particular level, collapsing into a Series. |
| **kwargs | any | None | No | This keyword has no additional effect but might be accepted for compatibility with Python NumPy. |
It returns DataFrame if the level parameter is specified; otherwise, Series is returned.
Let's take an example to understand the use of pandas.DataFrame.all() method. Following is the code that is executed by using the Jupyter notebook. If you are familiar with Jupyter, See the screenshot below.
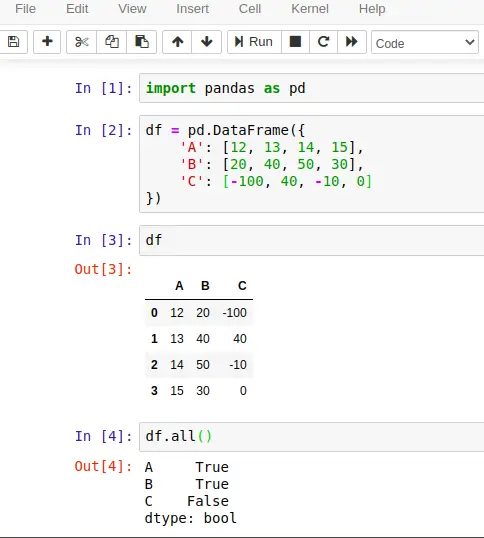
Let's check whether the given DataFrame contains zero or empty elements. The dataframe.all() method, by default check column-wise and returns False if any column contains zero or empty element. See the example here. This example is similar to the above code, executed by using Jupyter notebook. If you are not familiar with Jupyter then see this code to understand.
# import pandas library
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame of data
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [12, 13, 14, 15],
'B': [20, 40, 50, 30],
'C': [-100, 40, -10, 0]
})
# print dataframe
print(df)
print("\nApplying all() method...\n")
# all() method
df2 = df.all()
print(df2)
Output:
A B C
0 12 20 -100
1 13 40 40
2 14 50 -10
3 15 30 0
Applying all() method...
A True
B True
C False
dtype: bool
We can check for the zero or empty elements on the row-wise axis by setting the axis parameter as "columns" as we did in the below example.
# import pandas library
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame of data
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [12, 13, 14, 15],
'B': [20, 40, 50, 30],
'C': [-100, 40, -10, 0]
})
# print dataframe
print(df)
print("\nApplying all() method...\n")
# all() method
df2 = df.all(axis='columns') # row-wise checking
print(df2)
Output:
A B C
0 12 20 -100
1 13 40 40
2 14 50 -10
3 15 30 0
Applying all() method...
0 True
1 True
2 True
3 False
dtype: bool
In all the above examples, we get Series as a result but we can get DataFrame by setting the level parameter to the DataFrame.all() method. See the example here.
# import pandas library
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame of data
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [12, 13, 14, 15],
'B': [20, 40, 50, 30],
'C': [-100, 40, -10, 0]
})
# print dataframe
print(df)
print("\nApplying all() method...\n")
# all() method
df2 = df.all(level=0) # returns a DataFrame
print(df2)
Output:
A B C
0 12 20 -100
1 13 40 40
2 14 50 -10
3 15 30 0
Applying all() method...
A B C
0 True True True
1 True True True
2 True True True
3 True True False