

Python is a high-level, interpreted programming language, and is one of the most popular programming languages present in the software industry. One of the most important but often overlooked concepts in python is that of the break statement. Let us have a look at them in detail.
In python, the break statement is very much like their counterparts from other programming languages. It is usually used inside loops for conditional (or even unconditional) termination of execution of the loop and to resume execution from the statement just after the loop body.
In case the concept of loop nesting is involved, the execution of the innermost loop is terminated, as per the location of the break statement.
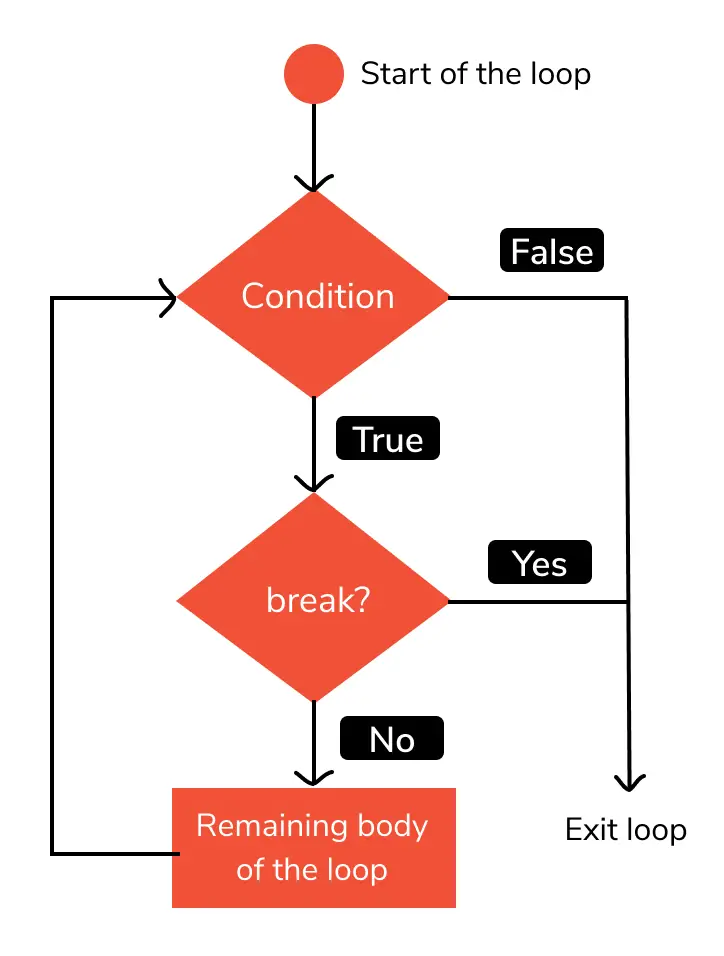
An advantage of the break statement is that it can be used with both for and while loops in similar ways. To have a conditional stoppage of loop execution, break statements are used with if statements and the desired conditions. The following flowchart would help us get a better understanding of the concept of break statements:
The syntax of break statements is very straightforward and is as follows. We simply use the keyword break.
loop(conditional-expression)
breakThe break statements can be used in the body of a while loop as well. In this example, we shall consider a variable i which is assigned an initial value of 0.
The main purpose of the body of the while loop is to print the current value of i for an iteration and then increment it or increase it by 1. The condition for the while loop to keep executing is i<3 which means that as long as the value of i is less than 3, the body of the while loop will keep getting executed.
Now, let us say we want to break this while loop in between, specifically when the value of i becomes 2. For this, we use a conditional break statement, that is, a break statement with an if statement. The condition for the if statement becomes i==2.
Let us look at the python code and corresponding output for this example -
# break with while loop in python
i=0
while i<3:
  if i==2:
    break
  print(i)
  i += 1Output
0
1
The break statements can be used in the body of a for loop as well. In this example, we shall consider the for loop to run from 0 to 4 which is specified using the range() function with a parameter 5.
The main purpose of the body of the for loop is to print the current value of i for an iteration and then increment it or increase it by 1.
Now, let us say we want to break this while loop in between, specifically when the value of i becomes 3. For this, we use a conditional break statement, that is, a break statement with an if statement. The condition for the if statement becomes i==3.
Let us look at the python code and corresponding output for this example -
# break with for loop in python
for i in range(5):
  if i == 3:
    break
  print(i)Output
0
1
2
An infinite loop is a very dangerous situation that is often overlooked but often causes problems during debugging.
Let us consider a case where a variable i is given an initial value of 2. We consider a while loop that has in its body a line to print the current value of the variable i and another line to increment it or increase it by 1. The twist here is that the condition to determine whether or not to execute the body of the while loop is i>1.
If you pay close attention you will realize that this condition is always going to result in a value of True being returned, thus causing the code to keep running in an infinite loop.
Let us look at the python code and corresponding output for this example:
# infinite while loop in python
i=2
while i>1:
  print(i)
  i+=1Output
2
3
4
5….infinitely
Now we shall see how the concept of a break statement works and proves helpful in this case, particularly a conditional break statement, using the if statement.
Let us say the condition to break out of the loop is that the value of i should become equal to 5. This is specified by the expression i==5.
Let us look at the python code and corresponding output for this example:
# break infinite loop in python
i=2
while i>1:
  if i==5:
    break
  print(i)
  i+=1Output
2
3
4
In this topic, we have learned the use and advantages of break statements in a Python program, following a running example of a simple iterative printing program, thus giving us an intuition of how this concept could be applied in real-world situations. Feel free to reach out to info.javaexercise@gmail.com in case of any suggestions.