

A DataFrame is the primary data structure of the Pandas library in Python and is commonly used for storing and working with tabular data.
A common operation that could be performed on such data is to use group by and sum on its column to extract more information.
To start working with Pandas, we first need to import it:
import pandas as pdLet us understand this operation with the help of an example. Consider the following DataFrame containing 3 students with names A, B, and C and their corresponding marks (out of 10) for two subjects, Mathematics and Physics.
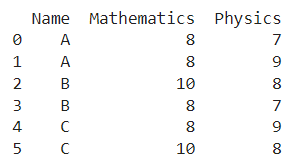
Code snippet for generating the above DataFrame:
# Importing required libraries
import pandas as pd
# Dictionary for our data
data = {'Name' : ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C'], 'Mathematics' : [8, 8, 10, 8, 8, 10], 'Physics' : [7, 9, 8, 7, 9, 8]}
# DataFrame for the dictionary
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data)
# PrintingÂ
print(df)Here, data is a dictionary we created to initialize the DataFrame. For this, we use the DataFrame() function of the Pandas library which takes the dictionary as an argument and returns the required DataFrame.
Now, let’s say we need to group the rows by the entry in the name column and sum their marks in the mathematics and physics columns respectively. The resulting output would look like this :
Let us look at different ways of performing this operation on a given DataFrame :
In this method, we use the groupby() function along with the sum() function. Inside the groupby() function, the label of the column that we need to group the rows by is the name.
Next, we apply the sum() function to this. The desired dataframe is obtained as the returned object. The changes are not made in an in-place manner therefore reassignment is required.
Let us take a look at the corresponding code snippet and generated output for this method:
# Importing required libraries
import pandas as pd
# Dictionary for our data
data = {'Name' : ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C'], 'Mathematics' : [8, 8, 10, 8, 8, 10], 'Physics' : [7, 9, 8, 7, 9, 8]}
# DataFrame for the dictionary
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data)
# Performing the operation
df = df.groupby(['Name']).sum()
# PrintingÂ
print(df)Output :

In this method, we use the groupby() function along with the agg() function. Inside the groupby function, the label of the column that we need to group the rows by is the name.
Next, we apply the agg() function to this, and the sum is passed as a parameter to this function. The desired dataframe is obtained as the returned object.
The changes are not made in an in-place manner therefore reassignment is required.
Let us take a look at the corresponding code snippet and generated output for this method:
# Importing required libraries
import pandas as pd
# Dictionary for our data
data = {'Name' : ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C'], 'Mathematics' : [8, 8, 10, 8, 8, 10], 'Physics' : [7, 9, 8, 7, 9, 8]}
# DataFrame for the dictionary
df = pd.DataFrame(data=data)
# Performing the operation
df = df.groupby(['Name']).agg('sum')
# PrintingÂ
print(df)Output :

In this topic, we have learned to use group by and sum in an existing Pandas DataFrame, following a running example of test scores of students in different subjects, thus giving us an intuition of how this concept could be applied in the real-world situations. Feel free to reach out to info.javaexercise@gmail.com in case of any suggestions.